


Cervical cancer ranks as the second most common cancer among women between 15 and 44 years of age.
Additionally, investigative detections by National Library of Medicine has evidently concluded that at least 15 high risks HPV genotypes contributes to the cause of cervical cancer and 6 low risks genotypes are most likely to cause warts around the body.
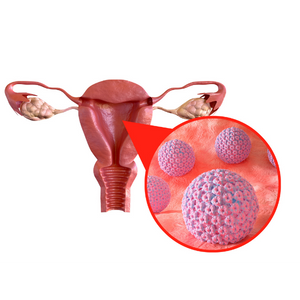
HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses, some of which are spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Sexually transmitted HPV types fall into two genotype groups, low and high risks. Low-risk HPVs do not cause diseases. However, a few low-risk HPV types can cause warts on or around the genitals, anus, mouth, or throat. High-risk HPVs are highly the cause of cervical cancers. Additionally, there are about 14 high-risk HPV types – in which two of these, HPV16 and HPV18, are responsible for most HPV-related cancers in at least 70% of women in Malaysia.
The reversible effect of HPV is hopeful, giving Malaysian women the freedom to seek early detection, protection and prevention. With this, LifeCare has introduced 3 main ways to protect and prevent Cervical cancer through Pap smear, HPV DNA Genotyping as well as Gardasil-9 Vaccination. These options are open to women who want to protect themselves based on their lifestyle choices.

Pap smear (or Pap test) is a cytological screening for cervical cancer. It involves collecting cells from the cervix in the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
Pap smears are recommended for women who are or have been sexually active, or who are 21 years of age and above. It is typically recommended that women get a Pap smear every 2 years, depending on their age, risk factors and previous diagnosis.

HPV DNA genotyping is a laboratory test that is used to identify the specific types of HPV present in a sample of cells or tissue, mainly to identify high-risk HPV genotypes, which are responsible for most HPV-related cancers.

3 doses of Gardasil-9 vaccines are used to prevent four types of HPV, such as HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18. prevent 2 types of low risk and 7 types of high risk – sub-types of HPVs.
The vaccine is typically given to adolescents and young adults between the ages of 9 and 26. It is most effective when given before an individual becomes sexually active, as this is when the risk of HPV infection is highest. Gardasil-9 has been shown to be highly effective in reducing the risk of HPV infection and the development of HPV-related cancers. With that, regular health screenings are still recommended to compliment the vaccination.




Consult with Dr Ramadas A/L Rajagovallu who provides comprehensive care for gynaecological conditions


Dr. Ramadas A/L Rajagovallu
Consultant Obstetrics & Gynaecologist
Life Care Diagnostic Medical Centre Sdn. Bhd. 200401034597 (673106-V)
Bangsar South
WhatsApp: 0122343610
1st Floor, Wisma Lifecare,
No. 5, Jalan Kerinchi, Bangsar South,
59200 Kuala Lumpur
Cheras South
WhatsApp: 01127213620
19A-2 & 19B-2, Block E, Kompleks Komersil Akasa,
Jalan Akasa, Akasa Cheras Selatan,
43300 Seri Kembangan, Selangor
Operating Hour:
Monday – Friday: 8.00am – 5.00pm
Saturday: 8.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & Public Holidays: Closed


Drop us your email to know more about our monthly deals and health tips!