
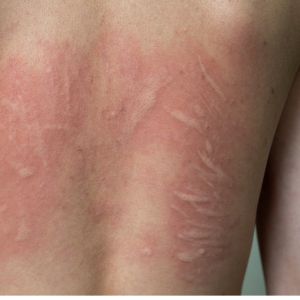
If you’re battling with urticaria, know that you’re not alone! Research reveals that urticaria is incredibly common, impacting up to 20% of the population, which means that 1 in 5 individuals will face it at some point in their lives.
Urticaria manifests as these intensely itchy, raised skin reactions called hives. These hives can take on various forms, such as being round, ring-shaped, or even joining together. They may appear in shades of pale, pink, or red. While they often adopt a circular appearance, they can crop up in diverse shapes and sizes, affecting any area of your body. Typically, each hive vanishes within 24 hours. However, don’t be surprised if new ones pop up in different spots.
In addition to urticaria, some individuals also experience a condition known as angioedema.
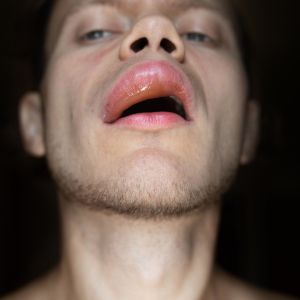
Angioedema mirrors hives but affects the deeper layers of your skin. This condition can lead to swelling in areas like your face, eyelids, ears, mouth, hands, feet, and genitalia. You might experience a sensation of fullness and discomfort in these affected areas.
Remember, urticaria can also be a component of a severe allergic reaction, which has the potential to be life-threatening! Your safety is paramount, so seek immediate medical attention if you suspect such a reaction.
Urticaria is caused by the release of chemicals from cells in the skin called mast cells. The main chemical is called histamine.
If you just got hives for the first time, you might have a new allergy to something.
Known triggers for acute urticaria include:
The itch stands out as the most troublesome symptom, and it can be extremely distressing. It has the potential to disrupt work, hinder sleep, and impact your social life significantly. When hives spread across your body, they can result in skin tightness and physical discomfort.
It’s worth noting that most individuals with urticaria are in good health. However, when angioedema is linked with urticaria, it can potentially affect your airway. This can give rise to breathing difficulties, necessitating immediate medical intervention! Your well-being is our top priority, so don’t hesitate to seek help if you encounter such a situation.
The diagnosis of urticaria can usually be made from the history and appearance, or description, of the hives. Your doctor will ask you questions and examine your skin thoroughly.
If an allergic reaction is suspected, a specific blood test for allergic sensitization or a skin prick test may be performed.
In chronic urticaria, a blood test may be necessary to ensure that there is no underlying medical condition such as thyroid disease or infection.
General measures include avoidance of triggers.

Are you among the many people in the Asia region who suffer from allergies? Allergens such as latex, food, grass pollens, tree pollens, mold, pets, pests, and mites can trigger mild to severe reactions. In Malaysia, allergy symptoms can be experienced throughout the year due to common triggers like house dust mites, molds, and pets being present in our environment. Identifying your allergens is the key to managing allergies.
RM 600
Life Care Diagnostic Medical Centre Sdn. Bhd. 200401034597 (673106-V)
Bangsar South
WhatsApp: 0122343610
1st Floor, Wisma Lifecare,
No. 5, Jalan Kerinchi, Bangsar South,
59200 Kuala Lumpur
Cheras South
WhatsApp: 01127213620
19A-2 & 19B-2, Block E, Kompleks Komersil Akasa,
Jalan Akasa, Akasa Cheras Selatan,
43300 Seri Kembangan, Selangor
Operating Hour:
Monday – Friday: 8.00am – 5.00pm
Saturday: 8.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & Public Holidays: Closed

