

Dietetic Department
August 17, 2021
Iron deficiency (lack of iron) is the most common cause of anaemia (lack of red blood cell in the body). Without enough iron, your body can’t produce enough haemoglobin, a substance in red blood cell that helps to carry oxygen to the body organs and tissues. This is why a person with anaemia may feel weak, tired, and irritable as the body is not able to carry enough oxygen.

Iron is essential during growth and development, pregnant women as well as people with certain health conditions.
Iron-deficiency anaemia can be treated with:
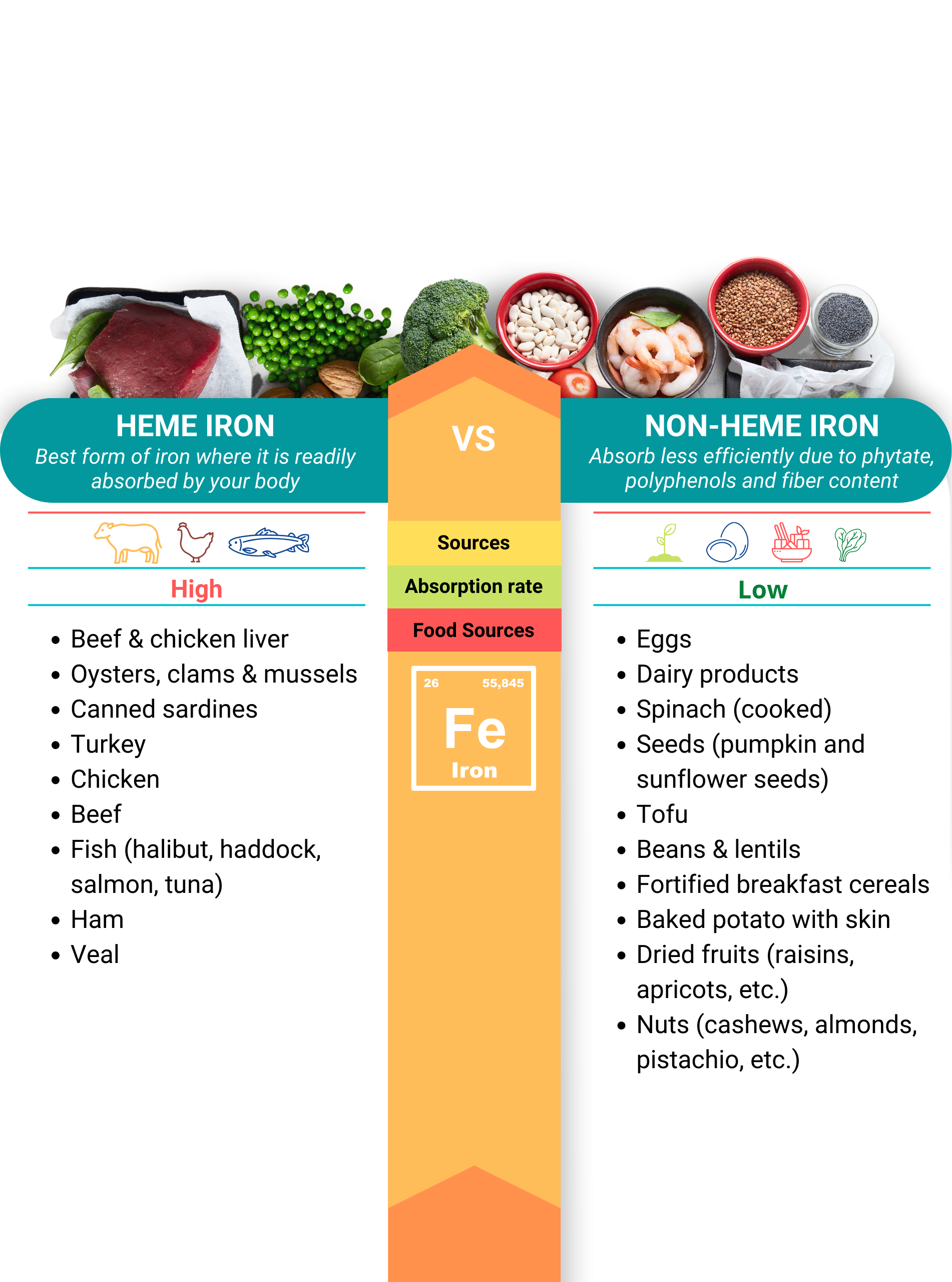
In foods, iron is present in two forms: heme and non-heme.
Heme iron is the best form of iron where it is readily absorbed by your body. Non-heme iron is absorbed much less efficiently due to its phytate, polyphenols and fiber content. For example, the iron absorption of a serving of steak is 20% whereas the iron absorption for a serving of cooked spinach is 1.4%. Therefore, it is very important for us to what are the dietary factors that can boost or inhibit the iron absorption in the body.
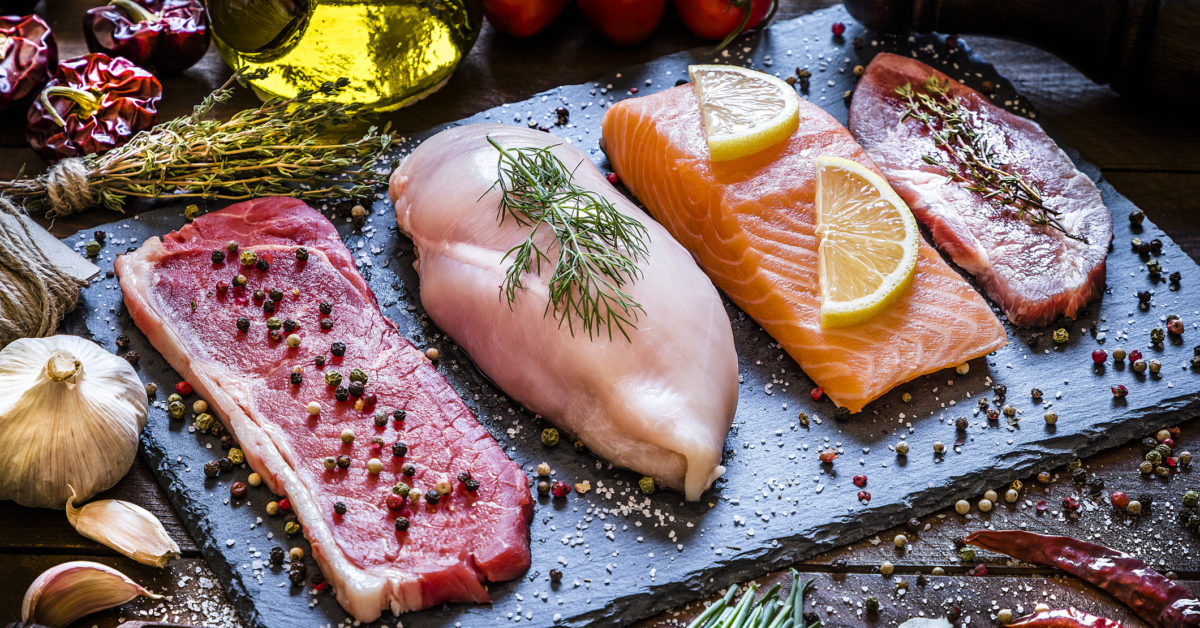
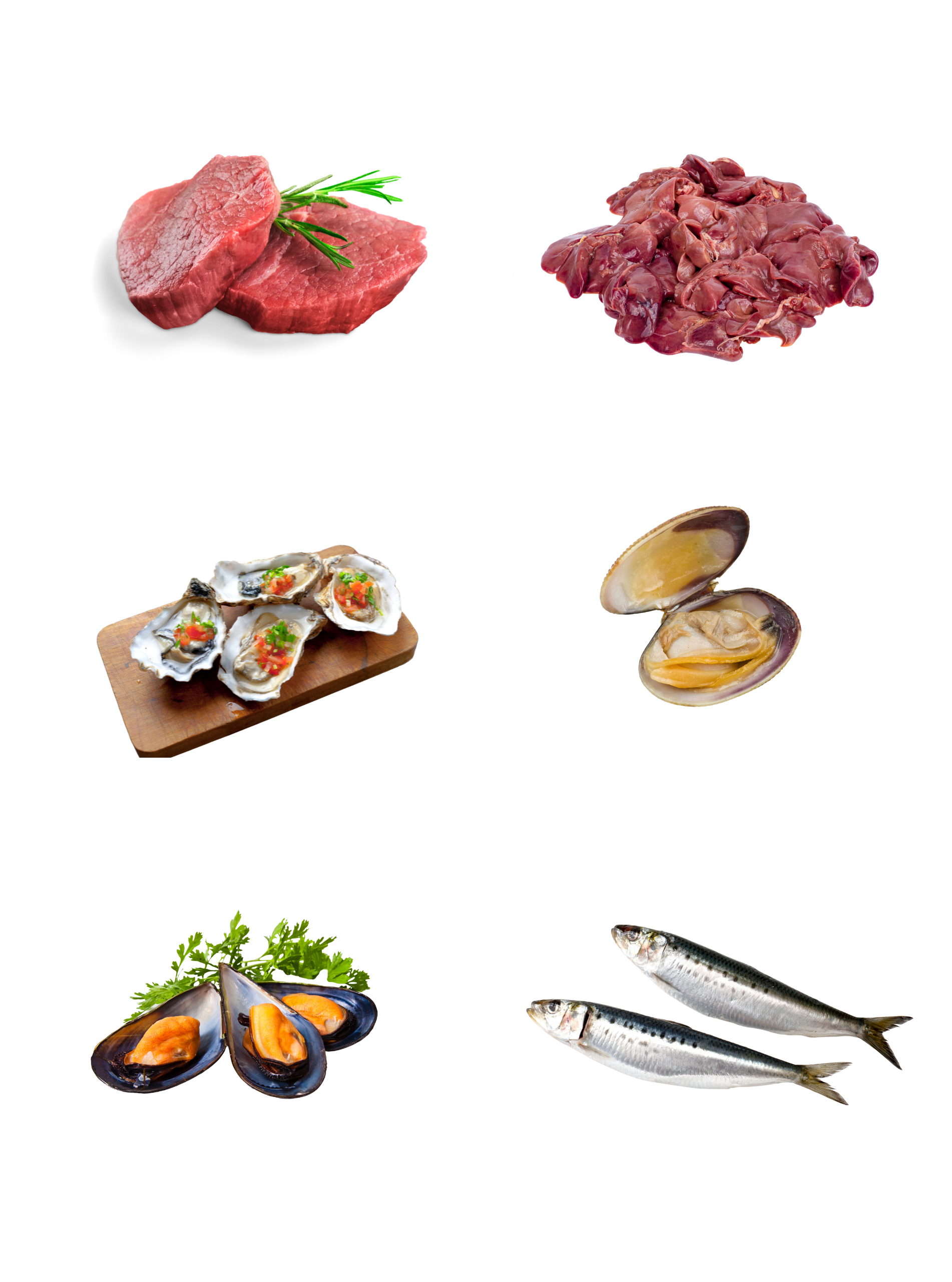



Animal only
Sources
Animal/Plant
High
Absorption rate
Low
Food sources
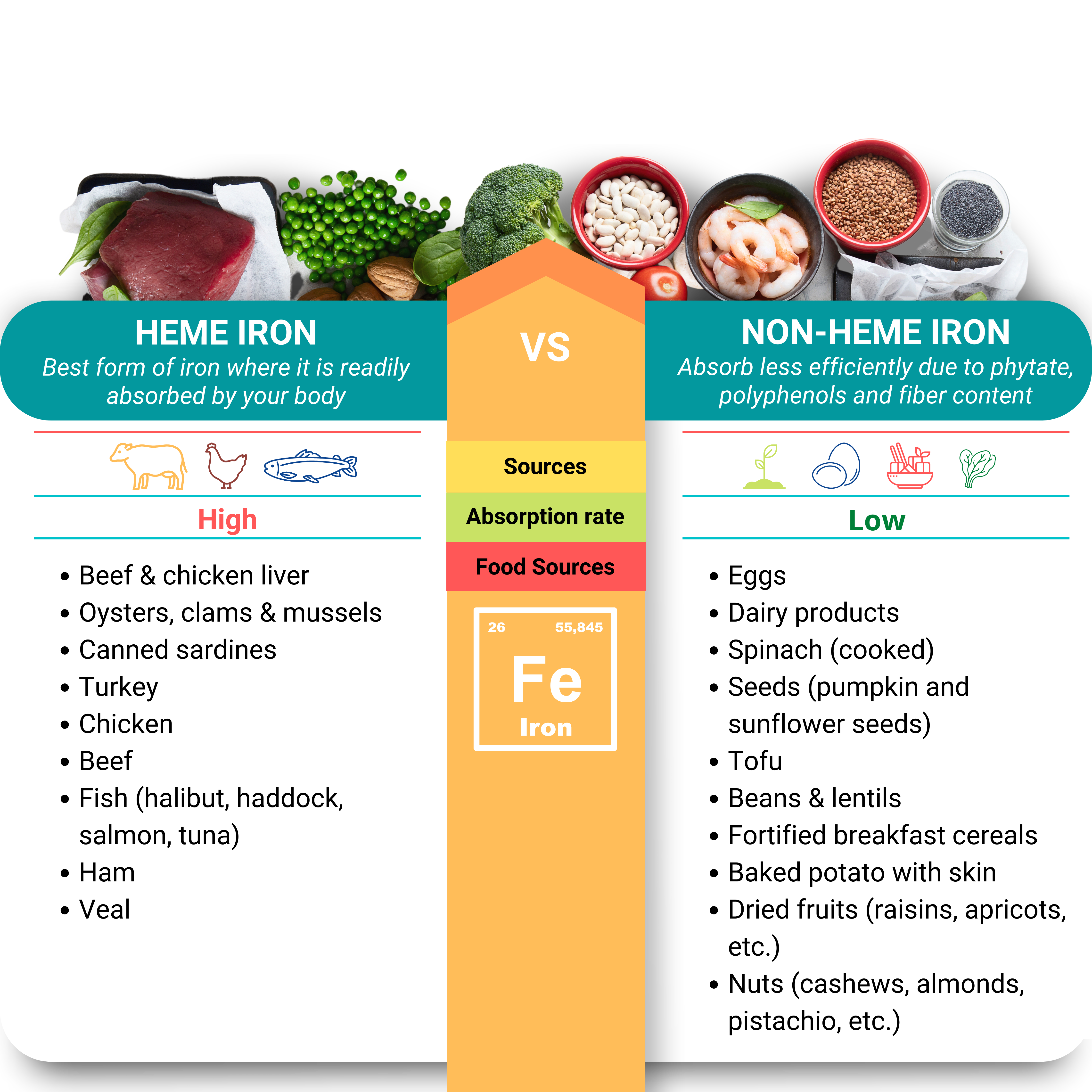
Source: Animal only
Absorption rate: High
Food Sources:
Sources: Animal/Plant
Absorption rate: Low
Food Sources:


Recommended for 30 years old and below. Package includes a range of blood & urine tests, cancer..
Life Care Diagnostic Medical Centre Sdn. Bhd. 200401034597 (673106-V)
Bangsar South
WhatsApp: 0122343610
1st Floor, Wisma Lifecare,
No. 5, Jalan Kerinchi, Bangsar South,
59200 Kuala Lumpur
Cheras South
WhatsApp: 01127213620
19A-2 & 19B-2, Block E, Kompleks Komersil Akasa,
Jalan Akasa, Akasa Cheras Selatan,
43300 Seri Kembangan, Selangor
Operating Hour:
Monday – Friday: 8.00am – 5.00pm
Saturday: 8.00am – 1.00pm
Sunday & Public Holidays: Closed